Stellarator turbulence optimization
Nuclear fusion and magnetic confinement
Nuclear fusion, the process by which light nuclei combine to form heavier ones, drives the energy output of stars. Whereas gravity naturally confines the fusion fuel (a hot hydrogen plasma) within stars, present-day fusion experiments and future power plants rely on strong toroidally-shaped magnetic fields for confinement.
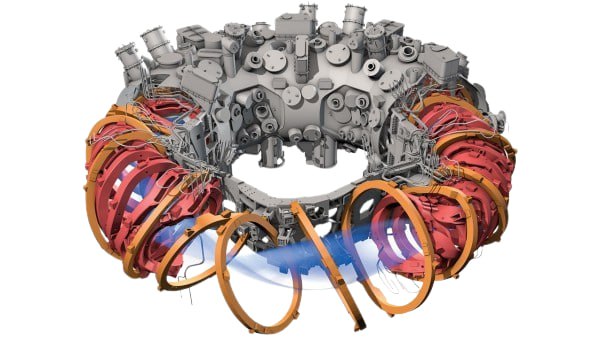
Stellarators
The stellarator is a reactor candidate that generates the magnetic field that contains the plasma by means of external magnets. The specific geometry of that magnetic field can be optimized to improve energy and particle confinement.
Turbulence optimization
Turbulent fluctuations of the plasma electromagnetic fields result in significant energy and particle losses. The primary objective of the present PhD project is to obtain new stellarator configurations that minimize turbulent losses. This endeavor is framed by first-principles theory and will be addressed through numerical simulation on super-computers and AI techniques.

If you are interested in nuclear fusion, theory and simulation, contact us with your CV and/or academic record at: jose.regana@ciemat.es and edi.sanchez@ciemat.es